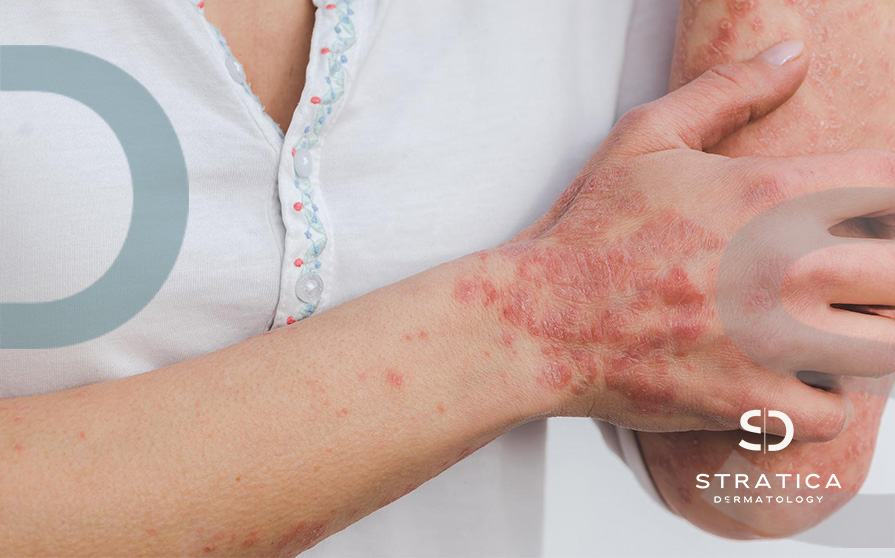
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes a rash with itchy, scaly patches, most commonly on the knees, elbows, trunk and scalp.
Psoriasis is a common, long-term (chronic) disease with no cure. It can be painful, interfere with sleep and make it hard to concentrate. The condition tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while.
Common triggers in people with a genetic predisposition to psoriasis include infections, cuts or burns, and certain medications.
Common Cause of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is thought to be an immune system problem that causes skin cells to grow faster than usual. In the most common type of psoriasis, known as plaque psoriasis, this rapid turnover of cells results in dry, scaly patches.
Common Psoriasis Triggers:
- Infections, such as strep throat or skin infections
- Weather, especially cold, dry conditions
- Injury to the skin, such as a cut or scrape, a bug bite, or a severe sunburn
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Certain medications — including lithium, high blood pressure drugs and antimalarial drugs
- Rapid withdrawal of oral or injected corticosteroids
How to treat Psoriasis
Psoriasis treatments aim to stop skin cells from growing so quickly and to remove scales. Options include creams and ointments (topical therapy), light therapy (phototherapy), and oral or injected medications.
Topical Therapy
- Corticosteroids
- Vitamin D analogues – Synthetic forms of vitamin D — such as calcipotriene (Dovonex, Sorilux) and calcitriol (Vectical)
- Retinoids. Tazarotene (Tazorac, Avage, others) is available as a gel or cream
- Calcineurin inhibitors. Calcineurin inhibitors — such as tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel)
- Salicylic acid
- Coal Tar
- Anthralin. Anthralin is a tar cream that slows skin cell growth.
Light Therapy
- Sunlight
- Goeckerman therapy – an approach that combines coal tar treatment with light therapy is called the Goeckerman therapy
- UVB broadband / narrowband
- Psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) – this treatment involves taking a light-sensitizing medication (psoralen) before exposing the affected skin to UVA light
- Excimer laser – with this form of light therapy, a strong UVB light targets only the affected skin
Oral or Injected medications
- Steroids
- Retinoids. Acitretin and other retinoids are pills used to reduce the production of skin cells
- Biologics. These drugs, usually administered by injection, alter the immune system in a way that disrupts the disease cycle and improves symptoms and signs of disease within weeks.
Examples are apremilast (Otezla), etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira), ustekinumab (Stelara), secukinumab (Cosentyx), ixekizumab (Taltz), guselkumab (Tremfya), tildrakizumab (Ilumya) and certolizumab (Cimzia)
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- Other medications. Thioguanine (Tabloid) and hydroxyurea (Droxia, Hydrea) are medications that can be used when you can’t take other drugs.